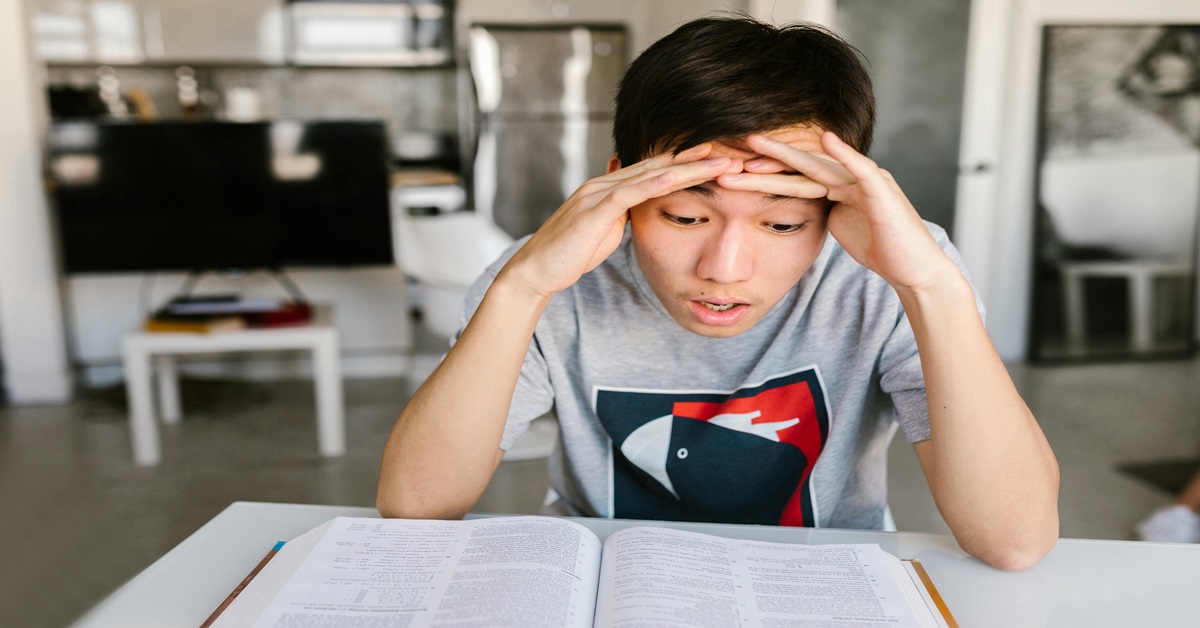
Stress and anxiety are common challenges faced by students at all educational levels. While a certain amount of stress can be motivating, excessive stress and chronic anxiety can negatively impact a student’s ability to learn and perform academically.
Understanding the effects of stress and anxiety on learning is crucial for educators, parents, and students in order to develop effective coping mechanisms and create supportive learning environments.
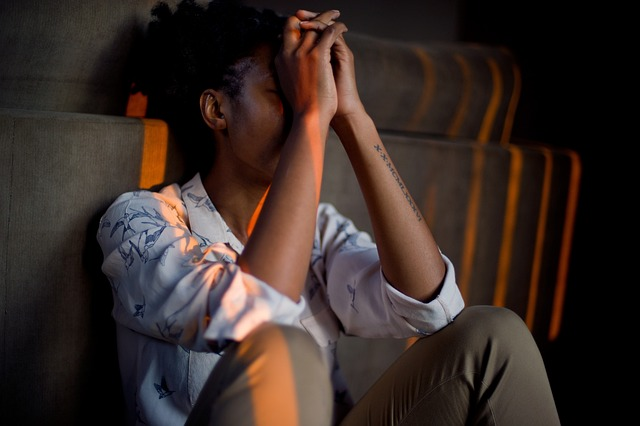

Photo courtesy: Pexels
Cognitive Impairment and Concentration Issues
One of the most immediate effects of stress and anxiety on students is the impairment of cognitive functions. High levels of stress can interfere with memory retention, problem-solving skills, and concentration. When students feel overwhelmed by academic pressures, they may struggle to focus in class, leading to poor comprehension and retention of material. Anxiety can also trigger overthinking, making it difficult for students to complete tasks efficiently.
Reduced Academic Performance
Studies have shown that students experiencing chronic stress and anxiety tend to perform poorly in exams and assignments. The constant state of worry affects their ability to recall information, solve complex problems, and manage time effectively. Test anxiety, a specific form of academic stress, can cause students to panic, resulting in underperformance even when they have adequately prepared.
Emotional and Behavioral Changes
Stress and anxiety can lead to significant emotional and behavioral changes in students. Feelings of frustration, helplessness, and self-doubt may arise, affecting their motivation and willingness to participate in class activities. Some students may become withdrawn, avoiding social interactions and group activities, while others may exhibit signs of irritability or defiance. These changes can further isolate students, exacerbating their anxiety and making it harder for them to seek help.
Physical Health Effects
Chronic stress and anxiety can take a toll on a student’s physical health. Symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, stomachaches, and muscle tension are common in students who are overwhelmed by academic pressures. Sleep disturbances, including insomnia and nightmares, can further impact their ability to focus and retain information. Poor physical health can create a cycle where students feel too exhausted to study, leading to further academic difficulties.
Impact on Social Development
Social interactions play a crucial role in a student’s learning experience. However, students who suffer from stress and anxiety may avoid engaging with their peers, leading to a lack of collaborative learning opportunities. They may also struggle with teamwork, communication, and problem-solving in group settings. This social withdrawal can limit their overall academic growth and reduce their confidence in interacting with others.
Long-Term Consequences
If left unaddressed, the effects of stress and anxiety on students can have long-term implications. Persistent academic struggles may lead to lower self-esteem, decreased motivation, and even school dropouts. In higher education, chronic stress can contribute to mental health issues such as depression, burnout, and severe anxiety disorders. These long-term consequences highlight the importance of early intervention and stress management strategies.
Strategies for Managing Stress and Anxiety
To mitigate the negative effects of stress and anxiety on learning, students, educators, and parents can implement various strategies:
- Time Management: Encouraging students to create structured schedules can help them manage their workload efficiently and reduce last-minute stress.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help students regulate stress levels.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and sufficient sleep can improve a student’s overall well-being and resilience against stress.
- Open Communication: Encouraging students to talk about their stressors with teachers, parents, or school counselors can provide emotional support and guidance.
- Positive Learning Environment: Educators can create a classroom atmosphere that reduces unnecessary stress by incorporating flexible teaching methods and fostering a supportive student-teacher relationship.
Conclusion
Stress and anxiety can significantly impact a student’s ability to learn, retain information, and perform academically. However, with the right support systems and coping mechanisms in place, students can develop resilience and effectively manage their stress levels. It is crucial for parents, teachers, and students themselves to recognize the signs of stress and anxiety early and take proactive steps to address them.
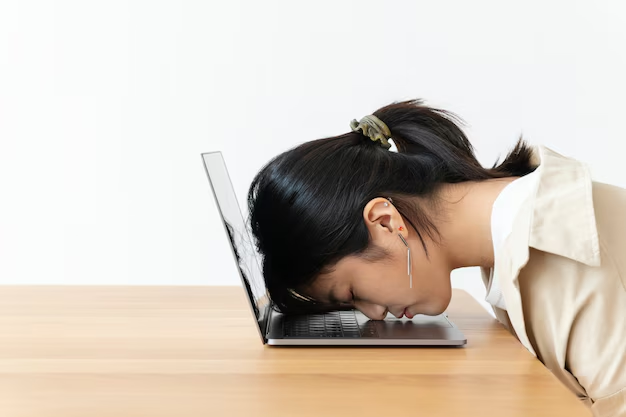

Photo courtesy: Pixabay
By fostering a positive and understanding learning environment, students can thrive academically and personally despite the pressures they may face.